- Manage Deployments >
- Edit a Deployment’s Configuration
Edit a Deployment’s Configuration¶
On this page
You can modify a deployment’s configuration and topology, including its MongoDB versions, storage engines, and numbers of hosts or shards. You can make modifications at all levels of a deployment’s topology from a top-level sharded cluster or replica set to lower levels, such as a replica set within a sharded cluster, or an individual process within a replica set. You can also modify standalone processes.
Considerations¶
Apply Changes to Cluster or Member¶
If you make configuration changes to an individual MongoDB process within a cluster, any future changes to the cluster no longer apply to the child process.
Example
If you turn off journaling for a replica set member and then later change the journal commit interval for the replica set, the change does not apply to the member.
MongoDB Version¶
To choose which versions of MongoDB are available to Cloud Manager, see Add a Custom MongoDB Build.
- Check the following documents for any considerations or
compatibility issues before changing a deployment’s MongoDB version:
- The MongoDB Release Notes
- The documentation for your driver.
- MongoDB Compatibility Matrix
- Plan the version change during a predefined maintenance window.
- Change the MongoDB version on a staging environment before changing a production environment. Your staging environment should mirror your production environment. This can help avoid compatibility issues that may result in downtime for your production deployment.
- Follow the MongoDB release notes when performing manual upgrades of replica sets and sharded clusters.
Downgrading Limitations
You cannot downgrade a MongoDB deployment:
- From version 3.6 to any version before 3.4.0
- From version 3.4 to any version before 3.2.8
Backup Considerations for MongoDB 4.2¶
Backup support for MongoDB
4.2 with "featureCompatibilityVersion" : 4.2 is extremely limited
at present. Support will be extended in future releases of Cloud Manager.
To learn more about backup considerations specific to MongoDB 4.2, see Backup Considerations.
If you choose to upgrade to MongoDB 4.2 with
"featureCompatibilityVersion" : 4.2, Cloud Manager displays a modal that
asks you to agree to the
special license
that MongoDB, Inc. grants to use MongoDB Enterprise for backups.
Storage Engine¶
Important
MongoDB removed support for the MMAPv1 storage engine in MongoDB 4.2. If you edit your deployment’s configuration to change your storage engine to WiredTiger Storage Engine, Cloud Manager restarts the MongoDB processes.
If you run or upgrade to MongoDB 3.0 or later and modify the MongoDB storage engine, Cloud Manager shuts down and restarts the MongoDB process. For a multi-member replica set, Cloud Manager performs a rolling initial sync of each member.
Cloud Manager creates backup directories during the migration from one storage engine to the other if the host has adequate disk space. If disk space is insufficient, no backups are taken. Cloud Manager does not delete the backup directories once the migration is complete. You can keep or delete the previous backup directories. The backup directories are located in the mongod’s data directory.
Example
If the data directory was /data/process, the backup would be
/data/process.bak.UNIQUENAME. The UNIQUENAME is a random
string that Cloud Manager generates.
Before you can change the storage engine for a standalone instance or replica set, you must give the Automation write access to the MongoDB data directory’s parent directory. The agent creates a temporary backup of the data in the parent directory when updating the storage engine. Storage engine changes on standalone instances also require adequate disk space to perform a full /mongodump and /mongorestore. This disk space is then restored to the instance after the storage engine configuration change. Cloud Manager does not delete the backup directories.
You cannot change the storage engine on a config server. For more information on storage engines and the available options, see Storage in the MongoDB manual.
Fixed Properties¶
You cannot modify the following settings after a deployment has been created:
database path- The hostname,
bind_iporportto which a MongoDB process is assigned
You can modify the following deployment settings:
log pathat the process level- advanced options
Deployment Topology¶
You can make modifications at all levels of a deployment’s topology, including child processes.
To modify the topology or processes, use this tutorial or one of the more specific tutorials:
Project-Level Modifications¶
Some modifications that affect a deployment occur at the project level. The following changes affect every MongoDB process in the project. For these changes, use the specified tutorials:
- To enable TLS for the deployment, see Enable TLS for a Deployment.
- To enable authentication for the deployment, see Enable Authentication for a Cloud Manager Project.
- To add or modify MongoDB users and roles for the deployment, see Manage MongoDB Users.
Multiple Modifications¶
You can combine multiple modifications into one deployment.
Example
You could make all the following modifications before clicking the Review Changes button:
- Add the latest stable version of MongoDB to the Add a Custom Build.
- Enable TLS for the deployment’s MongoDB processes.
- Add a new sharded cluster running the latest stable version of MongoDB from above.
When you click Review Changes, the review displays all the changes on one screen for you to confirm before deploying.
Force Reconfigure¶
For Replica Sets and Sharded Clusters Only
The MongoDB Agent can force a replica set to accept a new configuration
when you set the Force Reconfigure Replication Setting to
Yes. Only force a reconfiguration to recover a replica set from a
state in which a minority of its members are available.
Warning
Forcing a replica set reconfiguration might lead to a rollback of majority-committed writes.
Proceed with caution. Contact MongoDB Support if you have questions about the potential impacts of this operation.
See also
Reconfigure a Replica Set with Unavailable Members in the MongoDB Manual.
Removing a Shard¶
For Sharded Clusters Only
When you remove a shard, any unsharded databases in that shard are moved to a remaining shard using the movePrimary command.
All sharded collections remain online and available during the shard
removal process. However, read and write operations sent to unsharded
collections during the movePrimary operation can result in
unexpected behavior, including failure of the migration or loss of
data.
We recommend moving the primary shard for any databases containing unsharded collections before removing the shard.
To learn more about removing shards, see Remove Shards from an Existing Sharded Cluster.
Removing Multiple Replica Set Members¶
You can remove or migrate multiple replica set members at once, but a majority of the voting members must remain. If you need to remove more voting members, remove them one at a time.
Example
Example 1
You have a four-node replica set. All nodes are voting members. You can remove only one node, which preserves the majority of three out of four voting nodes. You can remove another node from the remaining three-node replica set afterward. This preserves the majority of the remaining voting nodes.
Example
Example 2
You have a four-node replica set. Three nodes are voting members and one node is a non-voting member. You can remove one voting member and one non-voting member at the same time. This preserves the majority of two out of three voting nodes.
To learn more about voting, see Replica Set High Availability and Replica Set Elections.
Prerequisites¶
Your deployment must be running a version of the Automation that is compatible with Cloud Manager. If your deployment is not running a compatible version of the agent, Cloud Manager displays a banner prompting you to update your agents.
Procedure¶
Select the type of deployment you want to edit:
- Standalone
- Replica Set
- Sharded Cluster
On the line listing the deployment item, click Modify.¶
Modify the Standalone Settings.¶
The Standalone Settings section contains the following configuration settings:
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Hostname | Hostname to which Cloud Manager deploys the mongod. This hostname
can be a hostname, an FQDN, an IPv4 address, or an IPv6
address. You can only deploy to hosts under Cloud Manager automation.
For complete documentation on adding servers to Cloud Manager
automation, see Provision Servers for Automation. |
| Port | Specify the IANA port
number for the The |
| Version | Select the MongoDB server version of the mongod process. |
| Auth Schema Version | Select the schema for storing the user for storing the user data for your deployment. If you are upgrading from a MongoDB version older than 3.0, MongoDB 3.0+ uses a different schema for user data than previous versions. For compatibility information, see the Security Changes in the MongoDB 3.0 release notes. |
| Feature Compatibility Version | Select the Feature Compatibility Version of the deployment. Cloud Manager displays this field if your deployment runs MongoDB version 3.4 or later. |
| Log File | Specify the full path to the Example Specifying The |
Modify Advanced Configuration Options.¶
The Advanced Configuration Options section allows you to set MongoDB runtime options for each MongoDB process in your deployment.
To add an option:
- Click Add Option.
- Click Select a Startup Option and select the configuration option.
- Cloud Manager displays a context-sensitive input for configuring an acceptable value for the selected option.
- Click Add to add the selected option and its corresponding value to the process.
For descriptions of the available Advanced Configuration Options, see Advanced Options for MongoDB Deployments.
Click Save.¶
Cloud Manager redirects you to the Deployment page, where you must review your changes before deploying the updated configuration.
Click Review & Deploy to review your changes.¶
Click Confirm & Deploy to deploy your changes.¶
Otherwise, click Cancel and you can make additional changes.
Navigate to the Deployment page for your project.¶
- If it is not already displayed, select the organization that contains your desired project from the Organizations menu in the navigation bar.
- If it is not already displayed, select your desired project from the Projects menu in the navigation bar.
- If it is not already displayed, click Deployment in the sidebar.
On the line listing the deployment item, click Modify.¶
Modify Cluster-Wide Settings.¶
The Replica Set Configuration section contains the following cluster-wide configuration settings.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Auth Schema Version | Select the schema for storing the user for storing the user data for your deployment. If you are upgrading from a MongoDB version older than 3.0, MongoDB 3.0+ uses a different schema for user data than previous versions. For compatibility information, see the Security Changes in the MongoDB 3.0 release notes. |
| Feature Compatibility Version | Select the Feature Compatibility Version of the deployment. Cloud Manager displays this field if your deployment runs MongoDB version 3.4 or later. |
| Replica Set Settings | Displays an table of each process associated with the replica set. You can configure the MongoDB server version, data directory, and log path of each process. |
| Process Name | Hostname and port of a Cloud Manager applies any settings configured for the replica set to all of its associated processes. |
| Version | Select the MongoDB server version of the mongod process. |
| Log File | Specify the full path to the Example Specifying The |
Configure Each Replica Set Member.¶
Cloud Manager lists each replica set member under the MongoD Settings heading of the Member Configuration section. Each replica set member has the following configurable options:
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Member | Select one of the following replica set member roles from the menu:
|
| Hostname | Select from the menu the host to which Cloud Manager Automation deploys the replica set member. The menu only lists hosts under Cloud Manager Automation. For complete documentation on adding servers to Cloud Manager Automation, see Provision Servers for Automation. This hostname can be a hostname, an FQDN, an IPv4 address, or an IPv6 address. |
| Port | Specify the IANA port
number for the The |
| Votes | Specify the number of votes that the replica set member has during
elections. This setting corresponds to the
votes mongod
replica set configuration option. |
| Priority | Specify the priority of the member during elections. Replica set
members with a priority of 0 cannot become the primary
and cannot trigger elections. This setting
corresponds to the
priority
mongod replica set configuration option. |
| Delay | Specify the number of seconds “behind” the primary member this
member should “lag”. This setting corresponds to the
slaveDelay
mongod replica set configuration option. |
| Build Indexes | Specify true to direct the mongod to build
indexes. This setting
corresponds to the
buildIndexes
mongod replica set configuration option. |
| Tags | Specify the tag or tags associated to the replica set.
This setting corresponds to the
For complete documentation on replica set tags, see Replica Set Tags |
| Add a Mongod | Adds an additional Adding a new |
Configure your Replication Settings.¶
The Replication Settings section contains the following configuration options for the replica set:
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Protocol Version | Select the replication protocol version used by the replica set.
This setting corresponds to the
For more information, see Replica Set Protocol Versions. |
| Chaining Allowed | Specify true to allow secondary
members to replicate from other secondary members. This setting
corresponds to the
chainingAllowed
replica set configuration option. |
| Write Concern Majority Journal Default | Determines the behavior of
{w:"majority"}
write concern if the write concern does not explicitly
specify the journal option
j. This setting corresponds to the
writeConcernMajorityJournalDefault
replica set configuration option. |
| Heartbeat Timeout (secs) | Specify the number of seconds that the replica set members wait for
a successful heartbeat from each other. This setting corresponds to
the heartbeatTimeoutSecs
replica set configuration option. |
| Election Timeout (ms) | Specify the time limit in milliseconds for detecting when a replica
set’s primary is unreachable. This setting corresponds to
the electionTimeoutMillis
replica set configuration option. |
| CatchUp Timeout (ms) | Specify the time limit in milliseconds for a newly elected
primary to sync, or catch up, with the other replica
set members that may have more recent writes. This setting
corresponds to the
catchUpTimeoutMillis
replica set configuration option. |
| CatchUp Takeover Delay (ms) | Specify the time in milliseconds a node waits to initiate a
catchup takeover after determining it is ahead of the
current primary. This setting corresponds to the
catchUpTakeoverDelayMillis
replica set configuration option. |
| Last Error Defaults | Specify the default write concern for the replica set. The replica set uses this write concern only when write operations or getLastError specify no other write concern. If this option is not set, the default write concern for the replica set only requires confirmation from the primary. Specify this option in the form of a document, i.e., |
| Force Reconfigure | Specify that you want to force a reconfiguration of the replica
set. When set to Warning Forcing a replica set reconfiguration might lead to a rollback of majority-committed writes. Proceed with caution. Contact MongoDB Support if you have questions about the potential impacts of this operation. See also Reconfigure a Replica Set with Unavailable Members in the MongoDB Server Manual. |
Modify Advanced Configuration Options.¶
The Advanced Configuration Options section allows you to set MongoDB runtime options for each MongoDB process in your deployment.
To add an option:
- Click Add Option.
- From the Select a Process Type menu, click the process for which you want to add an option.
- Click Select a Startup Option and select the configuration option.
- Cloud Manager displays a context-sensitive input for configuring an acceptable value for the selected option.
- Click Add to add the selected option and its corresponding value to every process of the selected process type in the cluster.
Cloud Manager lists each process in the cluster grouped logically. Click the grey arrow to the left of the logical grouping to display its sub-groupings and processes. You can modify the advanced options for each process individually as necessary.
For descriptions of the available Advanced Configuration Options, see Advanced Options for MongoDB Deployments.
Click Save.¶
Cloud Manager redirects you to the deployment page, where you must review your changes before deploying the updated configuration.
Click Review & Deploy to review your changes.¶
Click Confirm & Deploy to deploy your changes.¶
Otherwise, click Cancel and you can make additional changes.
Cloud Manager displays the following message if you attempt to force reconfigure a replica set.
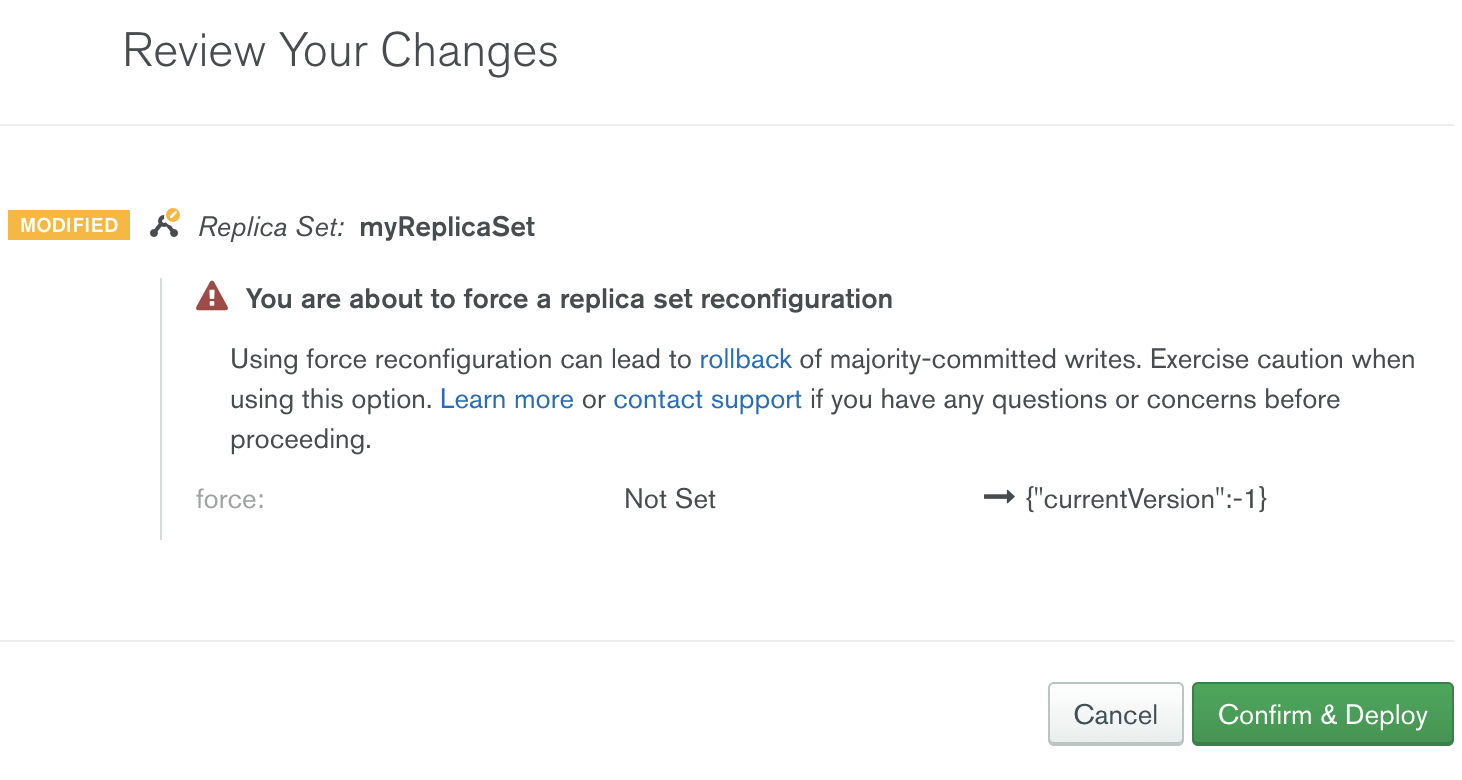
Before you click Confirm & Deploy, make sure that you understand the risks of force reconfiguring a replica set.
See also
Reconfigure a Replica Set with Unavailable Members in the MongoDB Manual.
Navigate to the Deployment page for your project.¶
- If it is not already displayed, select the organization that contains your desired project from the Organizations menu in the navigation bar.
- If it is not already displayed, select your desired project from the Projects menu in the navigation bar.
- If it is not already displayed, click Deployment in the sidebar.
On the line listing the deployment item, click Modify.¶
Configure Cluster-Wide Settings.¶
The Cluster Configuration section contains the following cluster-wide configuration settings.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Shard Name Prefix | Specify the prefix of each shard in the cluster. Cloud Manager
names each shard in the cluster using the <prefix_n> format,
where n is a 0-indexed, monotonically increasing integer. |
| Auth Schema Version | Select the schema for storing the user for storing the user data for your deployment. If you are upgrading from a MongoDB version older than 3.0, MongoDB 3.0+ uses a different schema for user data than previous versions. For compatibility information, see the Security Changes in the MongoDB 3.0 release notes. |
| Feature Compatibility Version | Select the Feature Compatibility Version of the deployment. Cloud Manager displays this field if your deployment runs MongoDB version 3.4 or later. |
| Process Name | Hostname and port of a Cloud Manager groups Note For clusters running MongoDB 3.0 or earlier, Cloud Manager groups
the config server |
| Version | Select the MongoDB server version of the mongod or mongos process. |
| Log File | Specify the full path to the Example Specifying The |
Configure Each Shard in Your Cluster.¶
From the Member Configuration section, click
Shard Settings to open the shard configuration
options. Cloud Manager lists each shard in the cluster and the mongod
processes associated to that shard. Each shard process has the
following options. You cannot modify options that are greyed out:
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Member | Select one of the following replica set member roles from the menu:
|
| Hostname | Select from the menu the host to which Cloud Manager Automation deploys the replica set member. The menu only lists hosts under Cloud Manager Automation. For complete documentation on adding servers to Cloud Manager Automation, see Provision Servers for Automation. This hostname can be a hostname, an FQDN, an IPv4 address, or an IPv6 address. |
| Port | Specify the IANA port
number for the The |
| Votes | Specify the number of votes that the replica set member has during
elections. This setting corresponds to the
votes mongod
replica set configuration option. |
| Priority | Specify the priority of the member during elections. Replica set
members with a priority of 0 cannot become the primary
and cannot trigger elections. This setting
corresponds to the
priority
mongod replica set configuration option. |
| Delay | Specify the number of seconds “behind” the primary member this
member should “lag”. This setting corresponds to the
slaveDelay
mongod replica set configuration option. |
| Build Indexes | Specify true to direct the mongod to build
indexes. This setting
corresponds to the
buildIndexes
mongod replica set configuration option. |
| Tags | Specify the tag or tags associated to the replica set.
This setting corresponds to the
For complete documentation on replica set tags, see Replica Set Tags |
| Add a Mongod | Adds an additional Adding a new |
To add additional shards to the cluster:
- Click Add a Shard.
- Under the Cluster Configuration section, set the
following parameters for each
mongodin the shard:- Version
- Data Directory
- Log File
Configure Each Configuration Server in Your Cluster.¶
Cloud Manager displays a different heading for your configuration server settings depending on the MongoDB version you selected for your configuration servers.
- MongoDB 3.2 or Later:
From the Member Configuration section, click Config Server Replica Set Settings to open the CSRS configuration options. Each config server replica set member has the following options:
Setting Description Member Select one of the following replica set member roles from the menu:
DefaultA data-bearing member of the replica set that can become the primary and vote in elections.
-
A non-data bearing member of the replica set that can vote in elections. Corresponds to the
arbiterOnlyreplica configuration option. -
A data-bearing member of the replica set that can vote in elections. Corresponds to the
hiddenreplica configuration option. -
A data-bearing member of the replica set that can vote in elections. Corresponds to the
slaveDelayandhiddenreplica configuration options.
Hostname Select from the menu the host to which Cloud Manager Automation deploys the replica set member. The menu only lists hosts under Cloud Manager Automation. For complete documentation on adding servers to Cloud Manager Automation, see Provision Servers for Automation.
This hostname can be a hostname, an FQDN, an IPv4 address, or an IPv6 address.
Port Specify the IANA port number for the
mongodprocess. This setting corresponds to thenet.portconfiguration file option. Defaults to27017.The
mongodmust have exclusive access to the specified port. If deploying multiplemongodprocesses to a single host, you must select a unique unused port for each process.Votes Specify the number of votes that the replica set member has during elections. This setting corresponds to the votesmongodreplica set configuration option.Priority Specify the priority of the member during elections. Replica set members with a priority of 0cannot become the primary and cannot trigger elections. This setting corresponds to theprioritymongodreplica set configuration option.Delay Specify the number of seconds “behind” the primary member this member should “lag”. This setting corresponds to the slaveDelaymongodreplica set configuration option.Build Indexes Specify trueto direct themongodto build indexes. This setting corresponds to thebuildIndexesmongodreplica set configuration option.Tags Specify the tag or tags associated to the replica set. This setting corresponds to the
tagsmongodreplica set configuration option.For complete documentation on replica set tags, see Replica Set Tags
Add a Mongod Adds an additional
mongodprocess as a replica set member.Adding a new
mongodprocess also updates the list of processes in the Cluster Configuration section. You must configure the Version, Data Directory, and Log File of the new process.- MongoDB 3.0 or Earlier
From the Member Configuration section, click Config Server Settings to open the configuration server options. Each configuration server has the following options:
Setting Description Hostname Select from the menu the host to which Cloud Manager Automation deploys the replica set member. The menu only lists hosts under Cloud Manager Automation. For complete documentation on adding servers to Cloud Manager Automation, see Provision Servers for Automation.
This hostname can be a hostname, an FQDN, an IPv4 address, or an IPv6 address.
Port Specify the IANA port number for the
mongodprocess. This setting corresponds to thenet.portconfiguration file option. Defaults to27017.The
mongodmust have exclusive access to the specified port. If deploying multiplemongodprocesses to a single host, you must select a unique unused port for each process.
Configure Each mongos in Your Cluster.¶
From the Member Configuration section, click
Mongos Settings to open the mongos
configuration options. Each mongos process has the
following options. You cannot modify options that are greyed out:
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Hostname | Select from the menu the host to which Cloud Manager Automation deploys the
This hostname can be a hostname, an FQDN, an IPv4 address, or an IPv6 address. |
| Port | Specify the IANA port
number for the The |
| Add a Mongos | Click to add an additional mongos process. |
Configure Each Replica Set in your Cluster.¶
The Replication Settings section contains the following configuration options for each replica set in the cluster:
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Protocol Version | Select the replication protocol version used by the replica set.
This setting corresponds to the
For more information, see Replica Set Protocol Versions. |
| Chaining Allowed | Specify true to allow secondary
members to replicate from other secondary members. This setting
corresponds to the
chainingAllowed
replica set configuration option. |
| Write Concern Majority Journal Default | Determines the behavior of
{w:"majority"}
write concern if the write concern does not explicitly
specify the journal option
j. This setting corresponds to the
writeConcernMajorityJournalDefault
replica set configuration option. |
| Heartbeat Timeout (secs) | Specify the number of seconds that the replica set members wait for
a successful heartbeat from each other. This setting corresponds to
the heartbeatTimeoutSecs
replica set configuration option. |
| Election Timeout (ms) | Specify the time limit in milliseconds for detecting when a replica
set’s primary is unreachable. This setting corresponds to
the electionTimeoutMillis
replica set configuration option. |
| CatchUp Timeout (ms) | Specify the time limit in milliseconds for a newly elected
primary to sync, or catch up, with the other replica
set members that may have more recent writes. This setting
corresponds to the
catchUpTimeoutMillis
replica set configuration option. |
| CatchUp Takeover Delay (ms) | Specify the time in milliseconds a node waits to initiate a
catchup takeover after determining it is ahead of the
current primary. This setting corresponds to the
catchUpTakeoverDelayMillis
replica set configuration option. |
| Last Error Defaults | Specify the default write concern for the replica set. The replica set uses this write concern only when write operations or getLastError specify no other write concern. If this option is not set, the default write concern for the replica set only requires confirmation from the primary. Specify this option in the form of a document, i.e., |
| Force Reconfigure | Specify that you want to force a reconfiguration of the replica
set. When set to Warning Forcing a replica set reconfiguration might lead to a rollback of majority-committed writes. Proceed with caution. Contact MongoDB Support if you have questions about the potential impacts of this operation. See also Reconfigure a Replica Set with Unavailable Members in the MongoDB Server Manual. |
Modify Advanced Configuration Options.¶
The Advanced Configuration Options section allows you to set MongoDB runtime options for each MongoDB process in your deployment.
To add an option:
- Click Add Option.
- From the Select a Process Type menu, click the process for which you want to add an option.
- Click Select a Startup Option and select the configuration option.
- Cloud Manager displays a context-sensitive input for configuring an acceptable value for the selected option.
- Click Add to add the selected option and its corresponding value to every process of the selected process type in the cluster.
Cloud Manager lists each process in the cluster grouped logically. Click the grey arrow to the left of the logical grouping to display its sub-groupings and processes. You can modify the advanced options for each process individually as necessary.
For descriptions of the available Advanced Configuration Options, see Advanced Options for MongoDB Deployments.
Click Save.¶
Cloud Manager redirects you to the deployment page, where you must review your changes before deploying the updated configuration.
Click Review & Deploy to review your changes.¶
Click Confirm & Deploy to deploy your changes.¶
Otherwise, click Cancel and you can make additional changes.